Smart Factory and Industrial Robots
KGS Solution Parts Support Changing Factory Requirements Towards Industry 4.0
Advancements in communication technologies have made it possible to transmit more data at high speeds, allowing industrial equipment to perform simple to complex tasks. In addition, the introduction of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in the factory setting is being considered to further improve productivity.
For example, in order to perform more complicated tasks, there is an increase in the number of moving parts within industrial robots; and it is necessary to accurately control those moving parts. And, more sensors, cameras, etc. are needed to perform these accurate control.
KITAGAWA INDUSTRIES America provide electromagnetic noise countermeasure technology (EMC), heat countermeasure technology (Thermal Interface Materials, or TIMs) for suppressing heat generated by electronic elements, and vibration countermeasure technology (Vibration Damping Materials) so that these industrial devices can operate accurately and safely.









Robot Arm
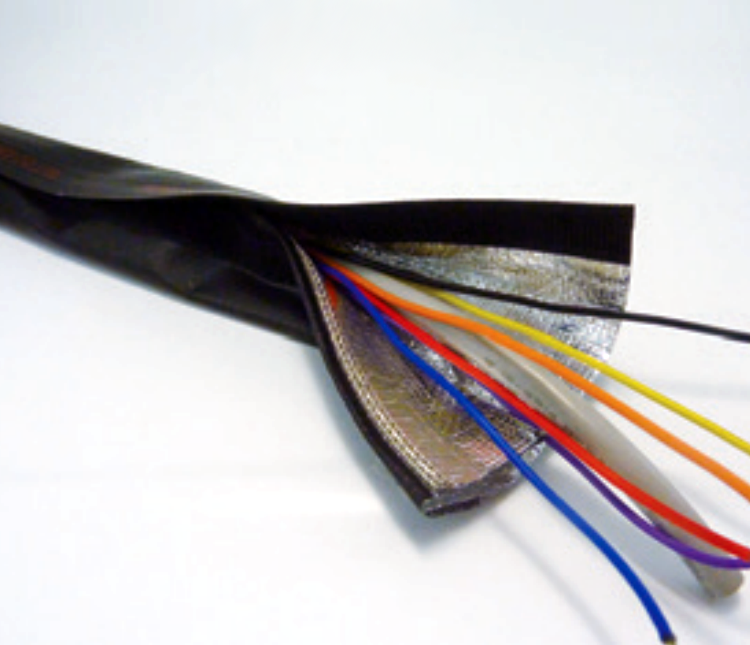
Robotic arms use motors of varying sizes in order to function. Wideband electromagnetic noise can emit from these motors as well as the signals that control them. KGS offers noise suppression solutions such as low-frequency and high-frequency ferrite cores including single piece types, clamp-types, flat cable cores, and flexible ferrite cores.
On moving apparatus like robotic arms, split-type ferrite cores are ideal and easy to attach onto cables. Cables between the robotic arm and its control panel (for motor control) can have a larger low-frequency ferrite core and a cable shield for insulation and EMI shielding.
Robot Arm
Robotic arms use motors of varying sizes in order to function. Wideband electromagnetic noise can emit from these motors as well as the signals that control them. KGS offers noise suppression solutions such as low-frequency and high-frequency ferrite cores including single piece types, clamp-types, flat cable cores, and flexible ferrite cores.
On moving apparatus like robotic arms, split-type ferrite cores are ideal and easy to attach onto cables. Cables between the robotic arm and its control panel (for motor control) can have a larger low-frequency ferrite core and a cable shield for insulation and EMI shielding.
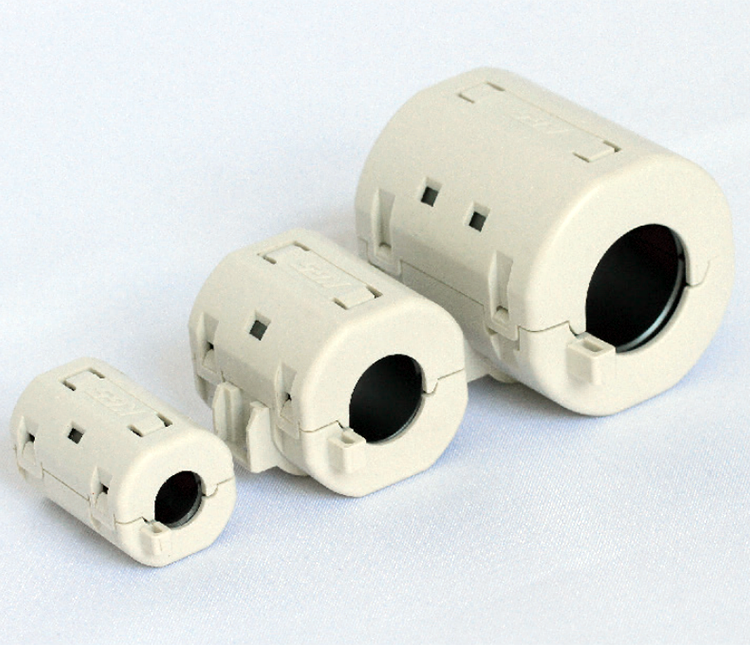
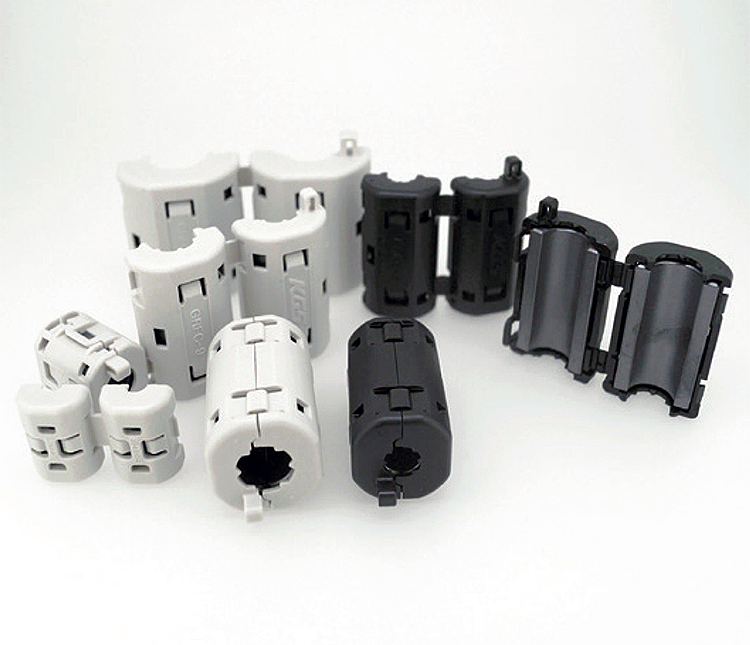
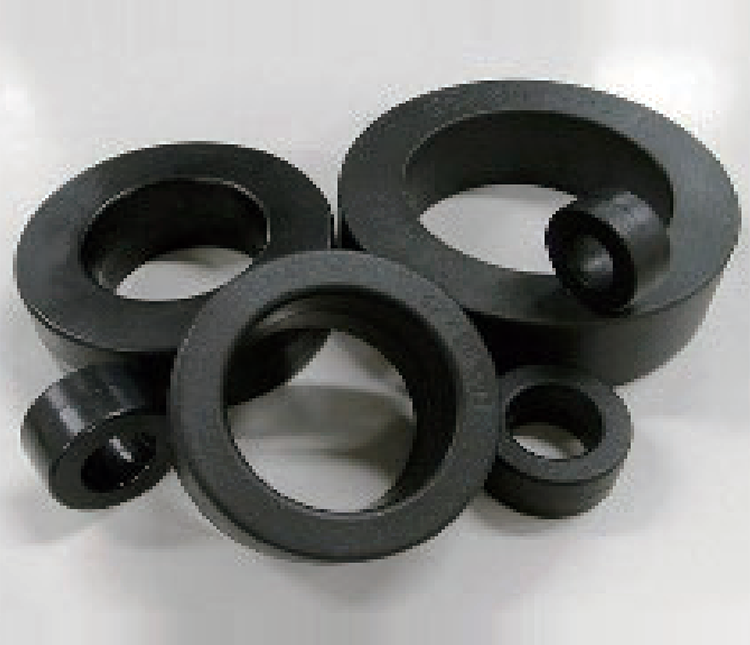
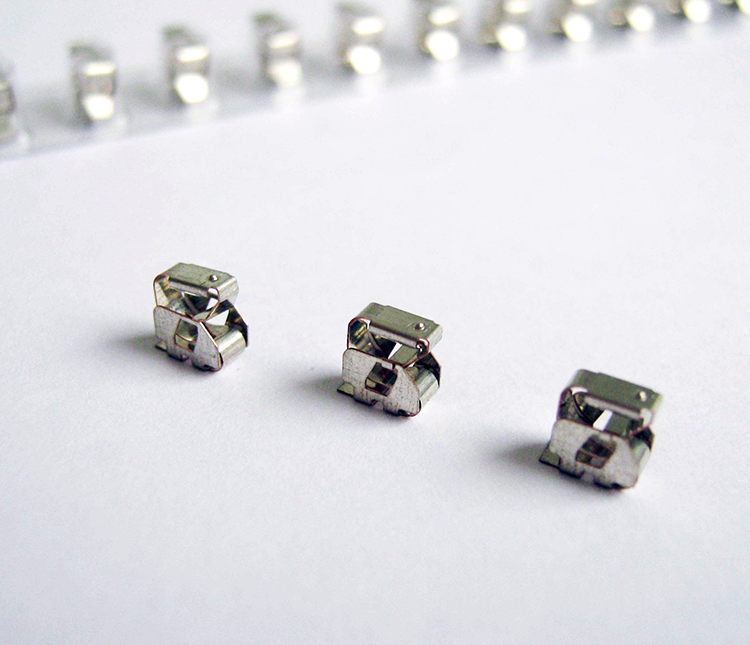
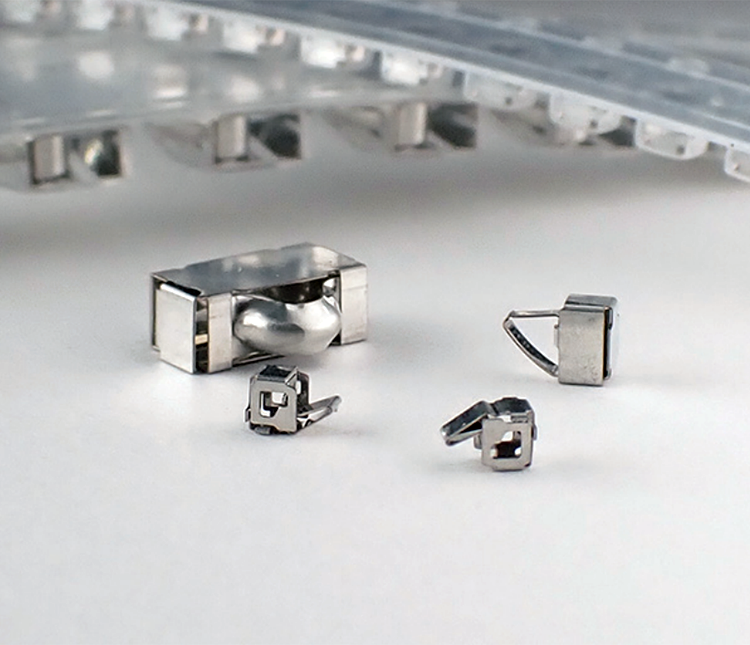
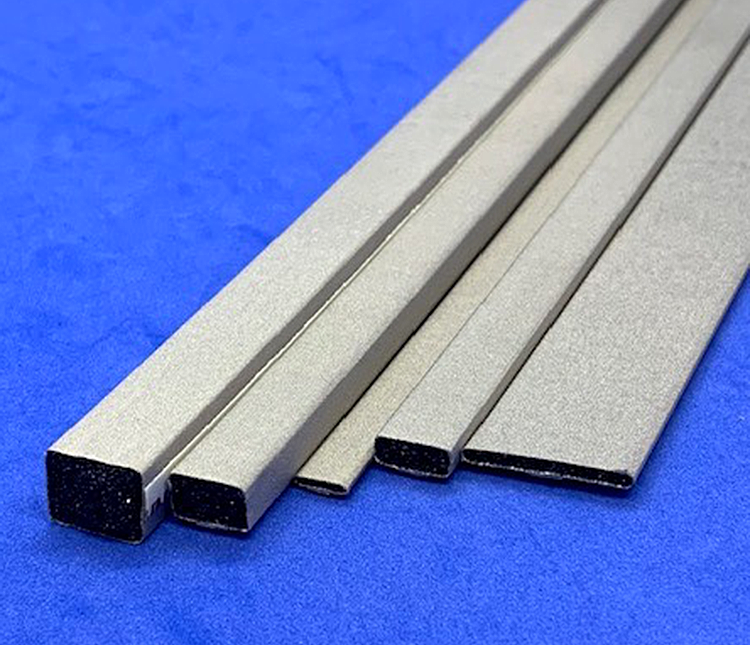
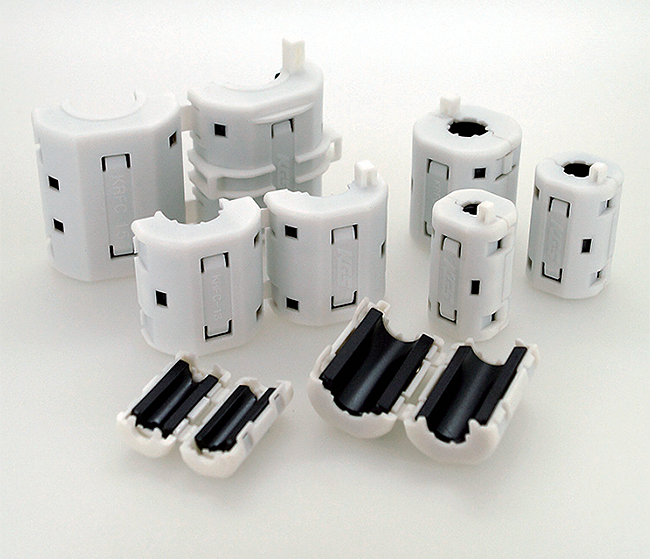
Ferrite Cores
Aimed to suppress low frequency noise between 150KHz to 30MHz. UL94V-0-rated housing.
Clamp-type high frequency noise
Employ high-performance ferrites (Nickel-Zinc) effective against high frequency noise.
Sleeve cores can be permanently attached to cables by thermostatic resin molding or heat shrink tubing.
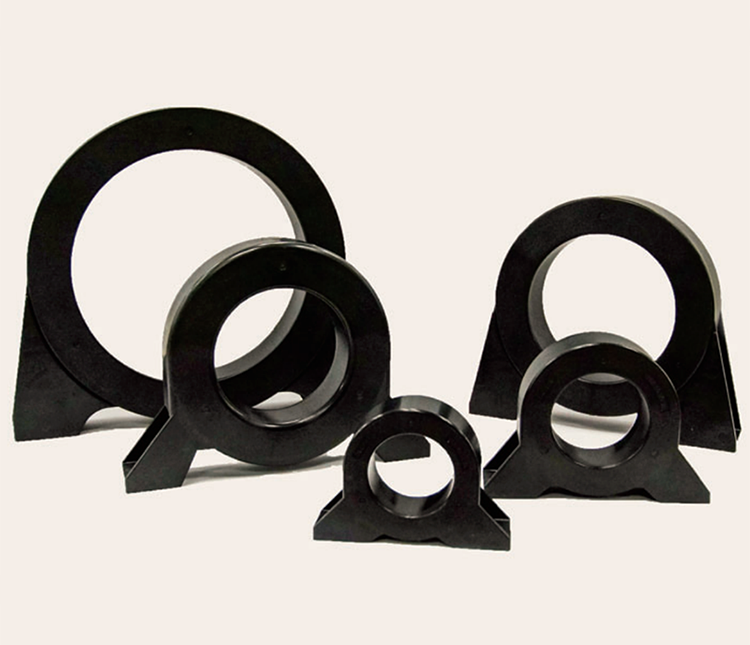
Broad Effect Core
Broadband EMC noise suppression
Amorphous metal core, effective for suppression of conducted and radiated broadband noise.
Includes screw mount tabs
High-performance noise suppression cores with secure screw-mounts for fixation.
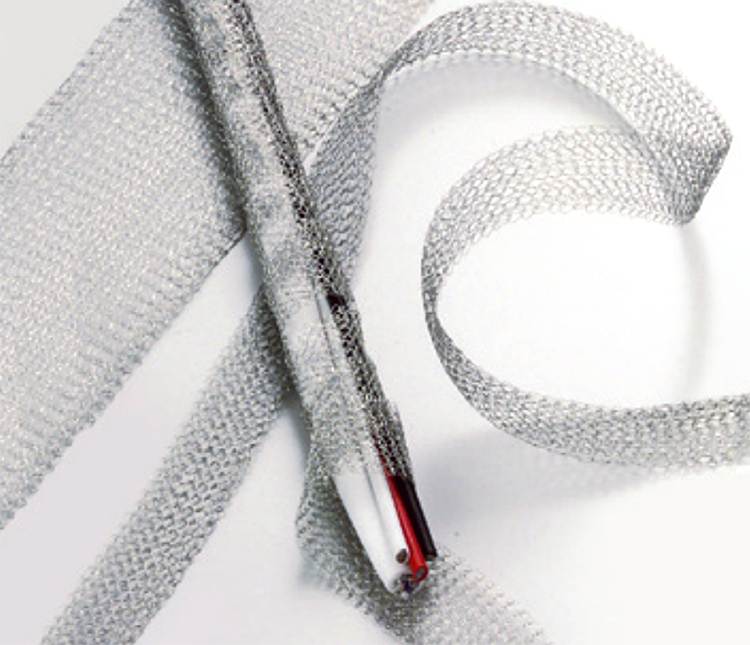
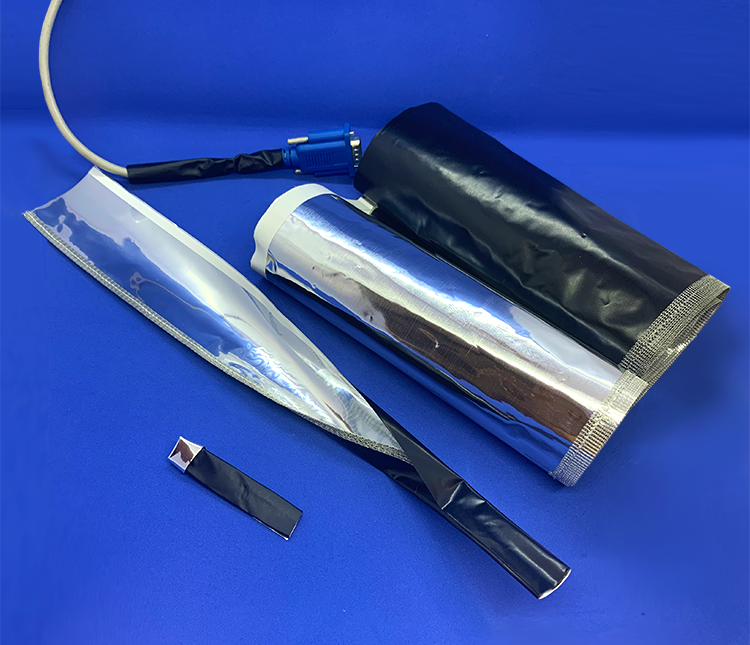
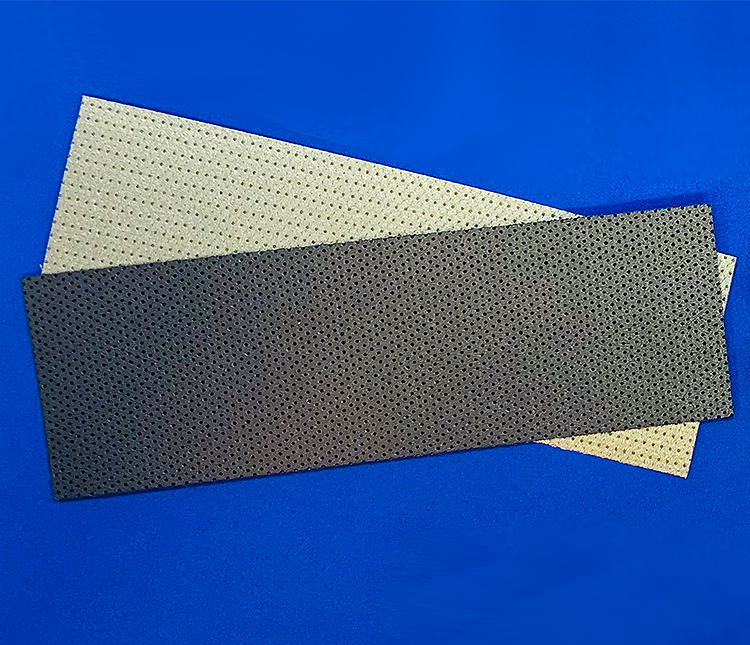
Cable Shielding
Wire Mesh Tape
Can be easily wrapped around the cable or insert cables through the mesh cylinder.
Flat Cable Shield Jacket
Light weight and flexible, nylon hook and loop (Velcro) fastener for easy application.
Smart Transport Robot
Smart transfer robots include sensors and sensor-related parts to transport goods autonomously. Existing electromagnetic noise and vibration movement from the factory machines can affect the robot’s performance, and immunity counter-measures would be important for accurate operations in such environments.
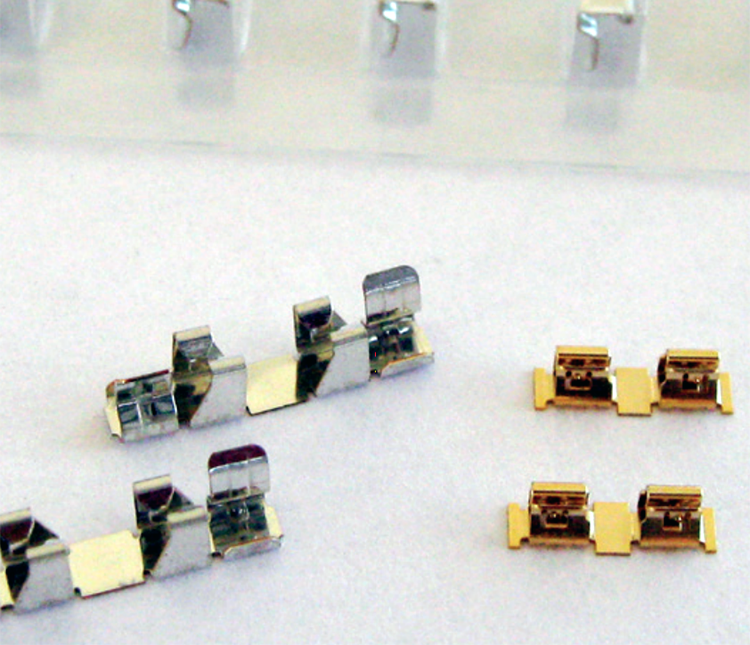
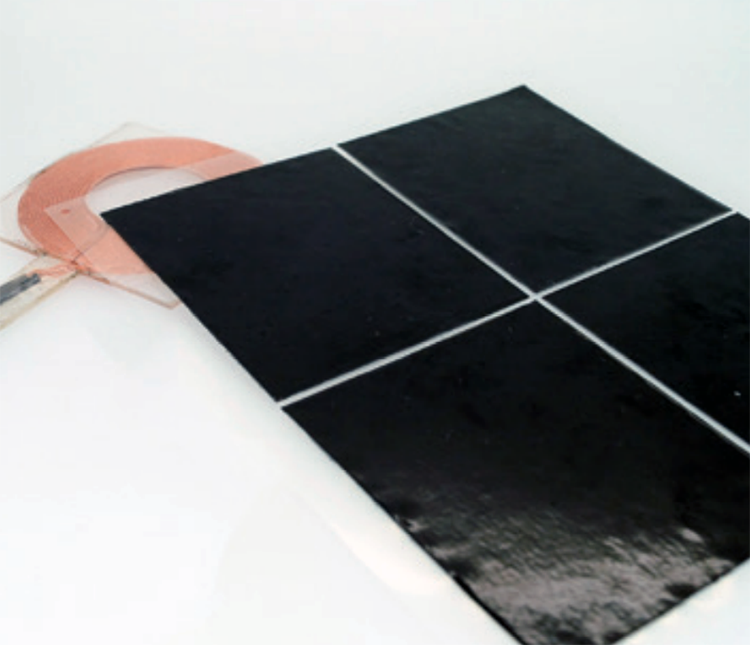
For EMC immunity noise mitigation, on-board grounding contacts (for EMC grounding and also effective against ESD or static electricity) and on-board shielding can clips (for use with shield cans) can be used. Thermal interface materials for transferring heat away from heat generating components to prevent overheating and malfunctions. EMI absorbers (such as flexible ferrite sheets for wireless charging) can also be used to combat immunity noise.
Smart Transport Robot
Smart transfer robots include sensors and sensor-related parts to transport goods autonomously. Existing electromagnetic noise and vibration movement from the factory machines can affect the robot’s performance, and immunity counter-measures would be important for accurate operations in such environments.
For EMC immunity noise mitigation, on-board grounding contacts (for EMC grounding and also effective against ESD or static electricity) and on-board shielding can clips (for use with shield cans) can be used. Thermal interface materials for transferring heat away from heat generating components to prevent overheating and malfunctions. EMI absorbers (such as flexible ferrite sheets for wireless charging) can also be used to combat immunity noise.
Control Box
Signal lines for motor control and power lines are contained together the control box, and EMC noise can conduct or radiate from these lines.
Ferrites are frequently used to suppress these noise, but understanding how to attach ferrites based on differential mode noise and common mode noise is an important distinction in addition to knowing the problematic frequency. There are also multiple openings where cables extend from the box and slits where the top and bottom of the box join together. Shielding materials such as conductive FoF gaskets and conductive foams can be used to fill these gaps.
Control Box
Signal lines for motor control and power lines are contained together the control box, and EMC noise can conduct or radiate from these lines.
Ferrites are frequently used to suppress these noise, but understanding how to attach ferrites based on differential mode noise and common mode noise is an important distinction in addition to knowing the problematic frequency. There are also multiple openings where cables extend from the box and slits where the top and bottom of the box join together. Shielding materials such as conductive FoF gaskets and conductive foams can be used to fill these gaps.
Signal lines for motor control and power lines are contained together the control box, and EMC noise can conduct or radiate from these lines.
Ferrites are frequently used to suppress these noise, but understanding how to attach ferrites based on differential mode noise and common mode noise is an important distinction in addition to knowing the problematic frequency. There are also multiple openings where cables extend from the box and slits where the top and bottom of the box join together. Shielding materials such as conductive FoF gaskets and conductive foams can be used to fill these gaps.
Broad Effect Core
Broadband EMC noise suppression
Amorphous metal core, effective for suppression of conducted and radiated broadband noise.
Includes screw mount tabs
High-performance noise suppression cores with secure screw-mounts for fixation.
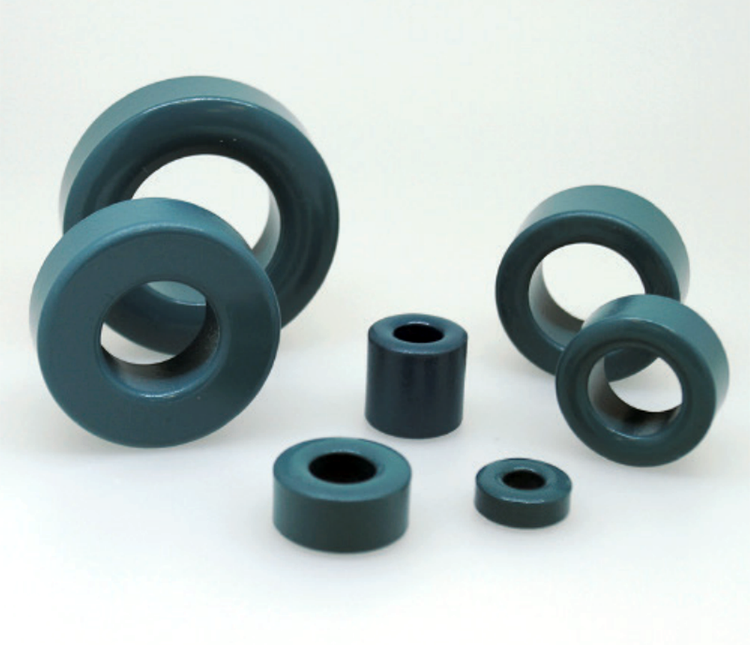
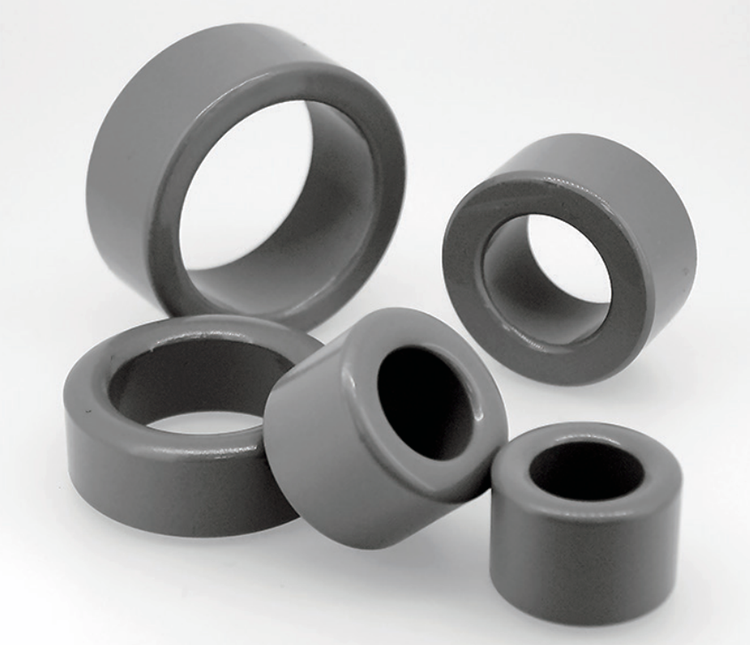
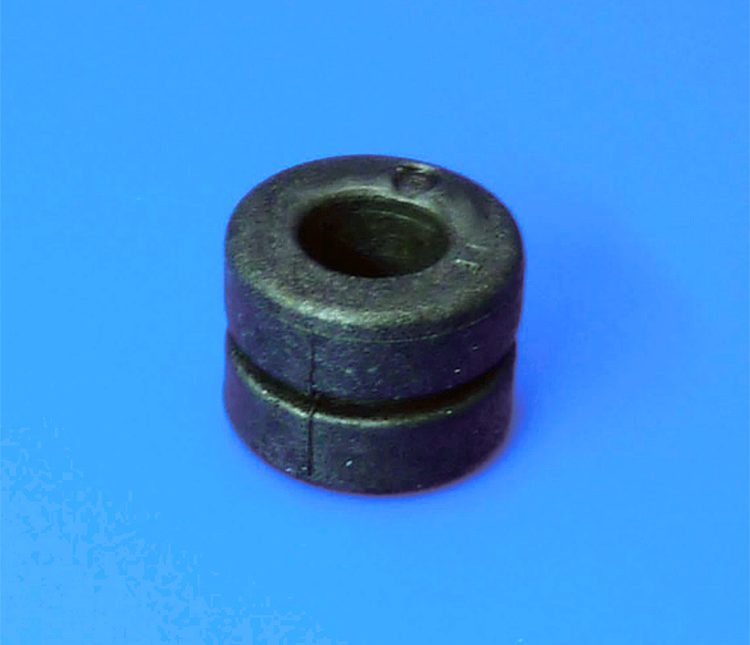
Ferrite Cores
Ni-Zn Ferrite Clamp
Effective suppression of conducted noise up to 30MHz and radiated noise over 30MHz.
Single, solid toroidal core
Effective for suppression of both conducted noise (up to 30MHz) and radiated noise (over 30MHz).
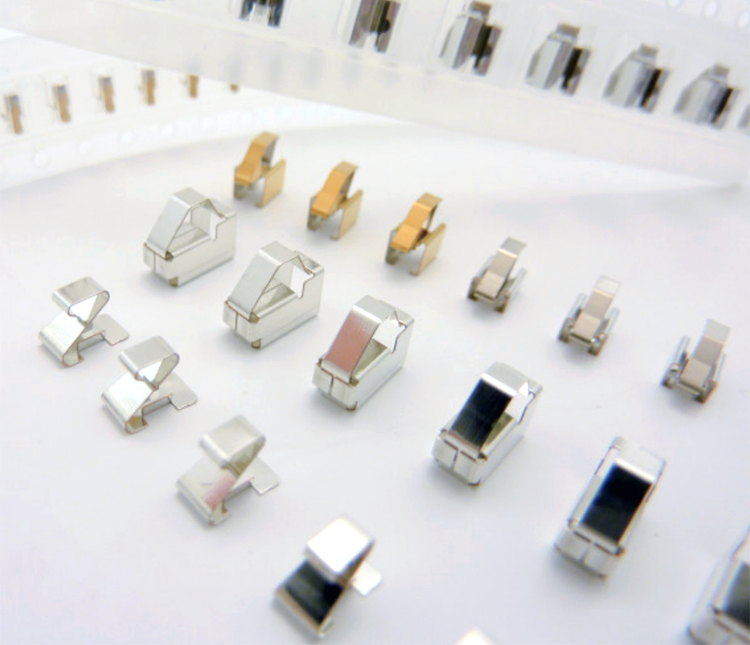
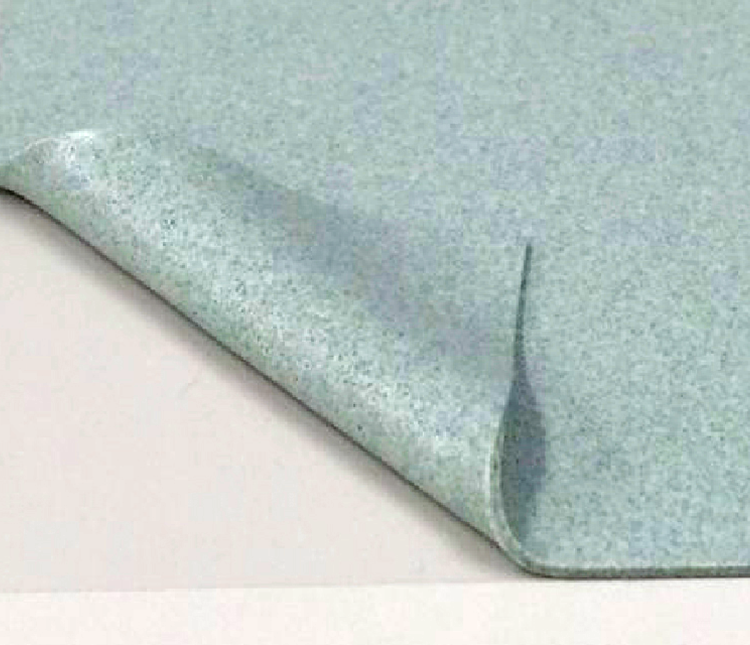
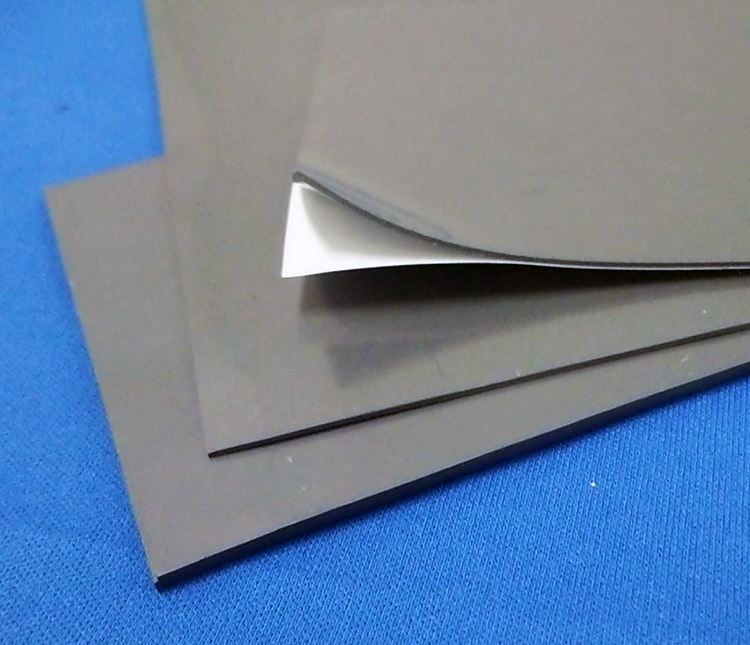
EMI Shielding
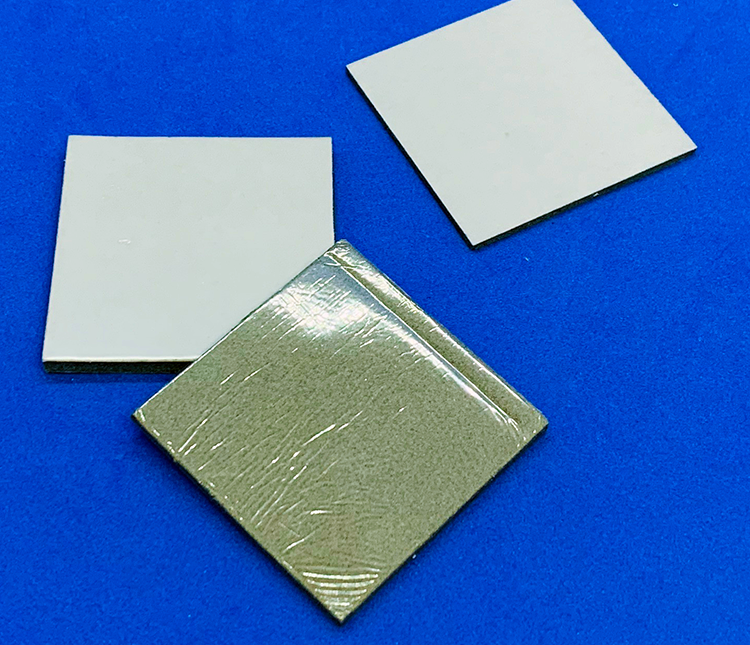
Fabric over the Foam Gasket
EMI gasket with low surface resistance for excellent shielding effectiveness and ESD mitigation.
Conductive Cushion Gasket
Ideal for grounding or shielding applications with narrow gaps and a great alternative to FoF gaskets.
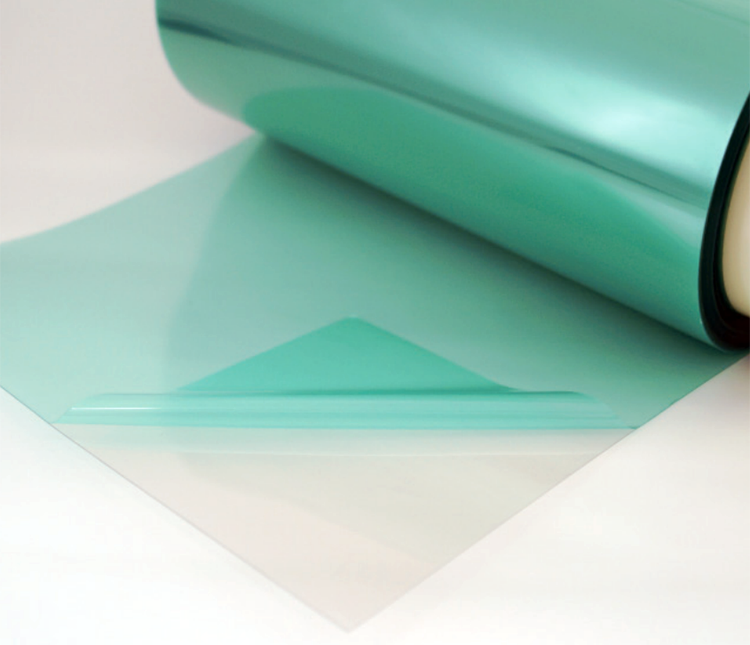
Transparent Conductive Film
Low surface electric resistance gives higher shielding effectiveness. Protected by PET film on both surfaces.
Lightweight Cable Shield Jacket
Easily installed on connected cables for immediate shielding against emissions or immunity noise.
Other FA Equipment
A wide variety of factory automation (FA) equipment exist to create a single product. These machines can bend, scrape, stretch, and even weld the raw materials to produce the final product. It becomes necessary to protect precision equipment in environments where vibration/shock from FA machines and water/oil used for processing materials can scatter.
EMC noise suppression and immunity mitigation solution materials are critical in these environments. Equally important in FA equipment are vibration damping materials to reduce vibration and shock, dust-proof and drip-proof parts at the cable opening, and protective materials for cables.
Other FA Equipment
Other FA Equipment
A wide variety of factory automation (FA) equipment exist to create a single product. These machines can bend, scrape, stretch, and even weld the raw materials to produce the final product. It becomes necessary to protect precision equipment in environments where vibration/shock from FA machines and water/oil used for processing materials can scatter.
EMC noise suppression and immunity mitigation solution materials are critical in these environments. Equally important in FA equipment are vibration damping materials to reduce vibration and shock, dust-proof and drip-proof parts at the cable opening, and protective materials for cables.